
Achmea
Implemented a new IFRS and Solvency II reporting chain including controls and dashboards.
IFRS 4 allowed significant diversity in practice across countries and products, limiting comparability both among insurers and versus other industries. IFRS 17 establishes consistent measurement based on current estimates, explicit risk adjustment and recognition of unearned profit via CSM only as services are provided.
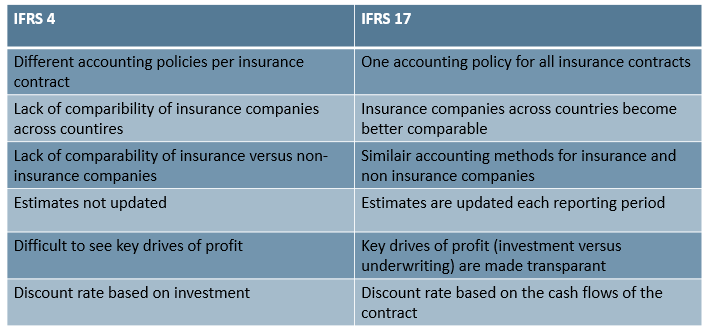
As an interim standard (2004), IFRS 4 preserved many legacy policies. Similar contracts could be measured differently between companies and jurisdictions, reducing comparability with non-insurance sectors.
It requires updated estimates (discount rates reflecting timing and financial risk) and a risk adjustment for non-financial risk. The CSM captures expected unearned profit and is released as service is provided — aligning with revenue recognition principles in other industries.
Implementation is costly and principle-based choices remain, so some variation will persist.
We help banks and insurers translate complex regulatory frameworks — IFRS 17, IFRS 9, Solvency II and ESG — into clear data models, reporting chains and actionable dashboards. With over 10 years of experience across Finance and IT, we bridge the gap between strategy and implementation.

Implemented a new IFRS and Solvency II reporting chain including controls and dashboards.

Adjusted MRAP, Solvency II and SOx controls to comply with new regulations; supported multiple reporting periods.

Supported integration of data streams between ASR and Aegon.
Years of insurance reporting experience: accounting policies, bookkeeping and IFRS 17 reporting.
Certified in analysis frameworks (e.g., BABOK / BCS). We translate IFRS into clear requirements and data elements.
Data warehousing and engineering expertise to design pragmatic, robust implementation strategies.